aop可以方便我们在程序中加入各种和业务无干扰的程序代码. 比如 日志,缓存, 监控, 事务等等
但是有一个点往往会让很多同学忽略, 就是对象内部的方法自己调用时是不会被aop切入的.
参考文档 https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.2.x/spring-framework-reference/core.html#aop-understanding-aop-proxies
方法内部调用流程
(时序图1)这种场景的执行流程如下
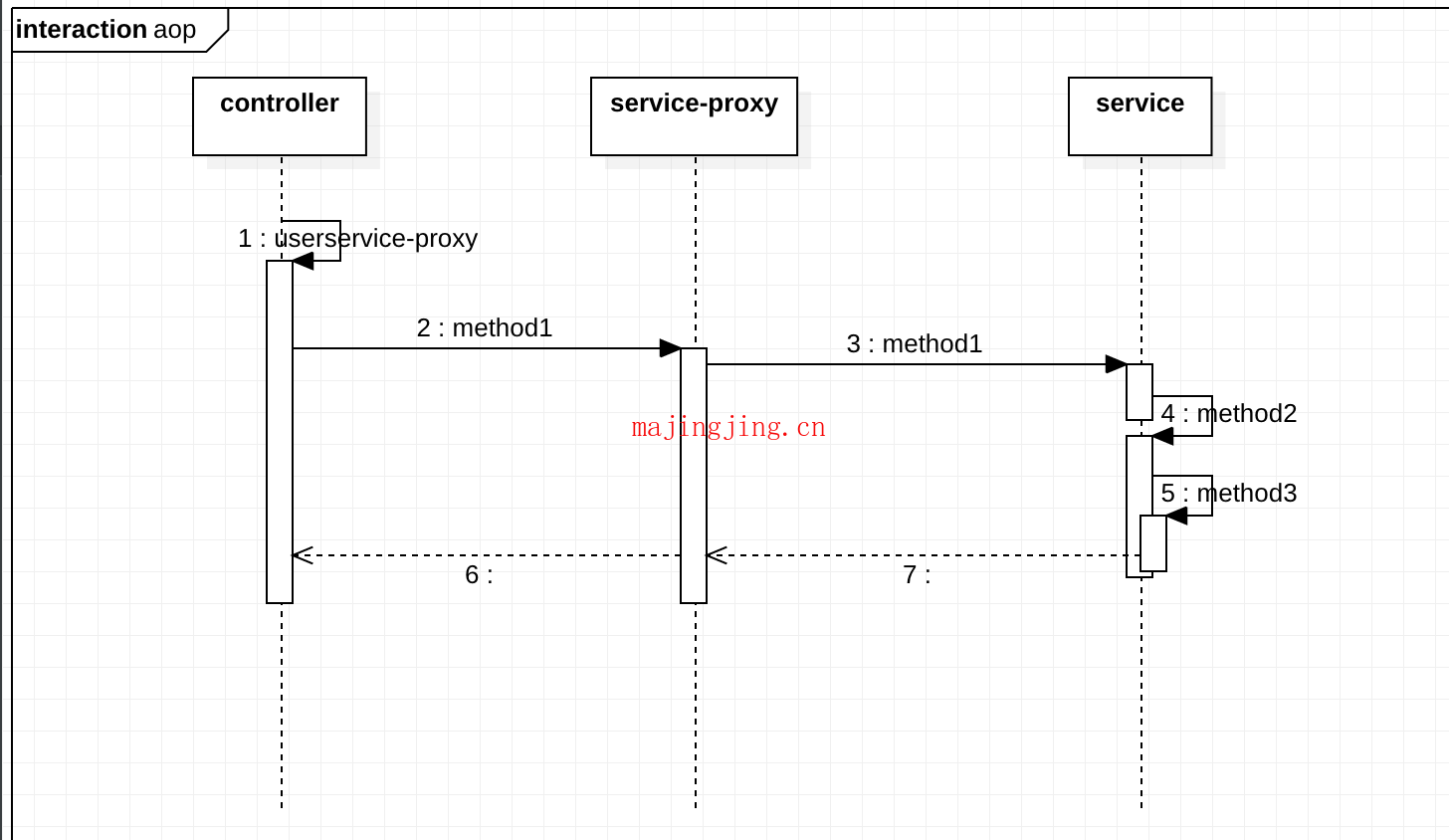
aop能做到拦截到流程
(时序图2)其实我们真实希望的执行流程如下, 这样才能保证我们的aop程序能够执行正常
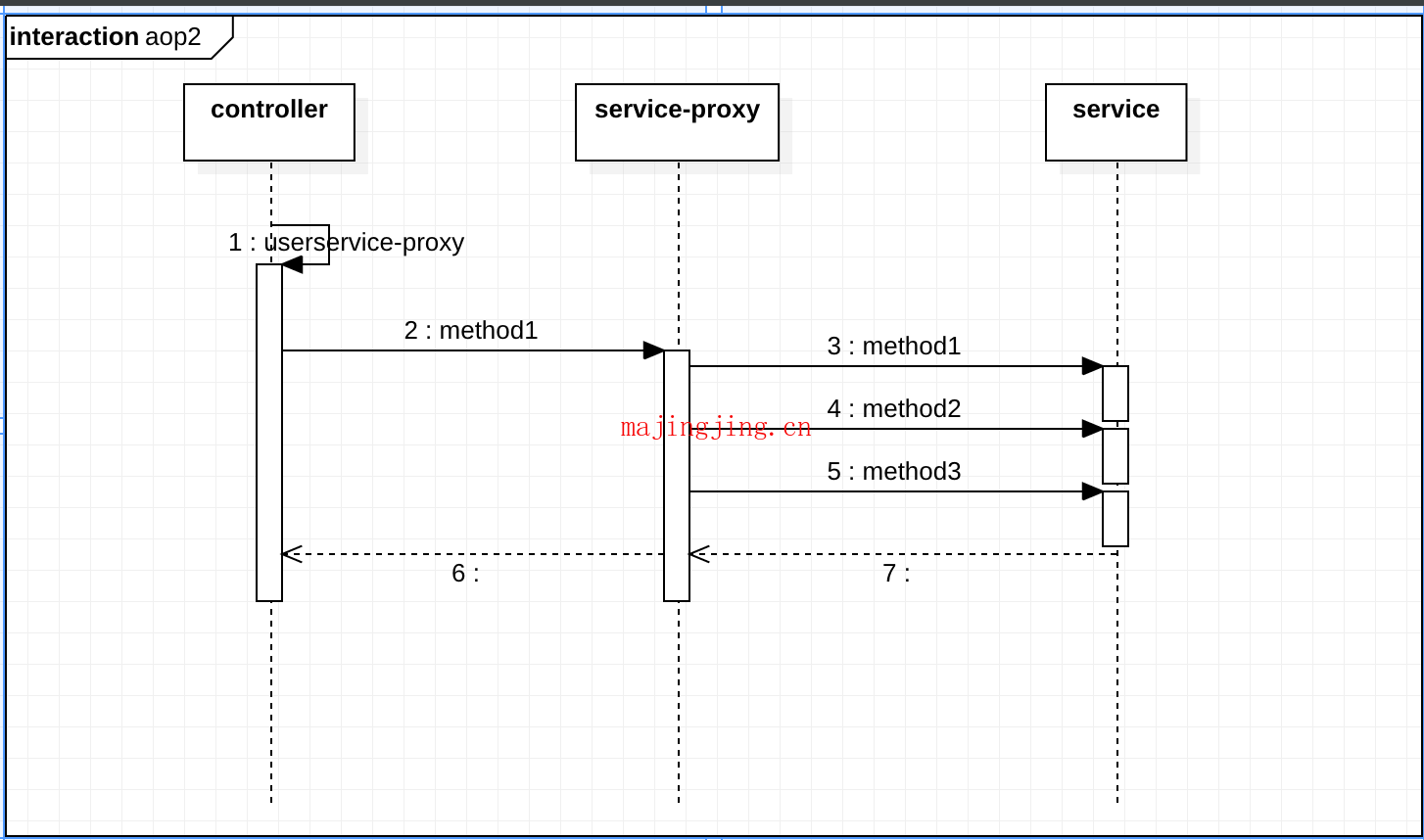
看完这两个流程我们就很清楚, 为什么方法内部的调用aop会失效,以及如何调整.
场景示例代码
下面我们来写个具体的示例来描述这种场景. 1 构建一个spirng-boot程序, 加入aop依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
</dependency>
2 编写 LogToken 注解, 和Aop程序
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface LogToken {
}
package cn.majingjing.demo.aop.config;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @Author JingjingMa
* @Date 2019/9/15 12:47
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAop {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogAop.class);
/**
* 定义AOP扫描路径
* 第一个注解只扫描aopTest方法
*/
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(cn.majingjing.demo.aop.config.LogToken)")
public void log() {
log.info("---LogAop-log()---");
}
@Around("log()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String methodName = method.getName();
log.info(className+" "+methodName+"\tstart");
Object proceed;
proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
log.info(className+" "+methodName+"\tover");
return proceed;
}
}
3 编写业务代码 LogService1
@Service
public class LogService1 {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogService1.class);
@LogToken
public void method1() {
log.info("hello method1");
}
@LogToken
public void method2() {
log.info("hello method2");
this.method1();
}
}
4 启用 aop的代理
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(MainApplication.class).run(args);
}
}
5 编写单元测试代码,运行,观察结果
package cn.majingjing.tm.blog.majjblogweb;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = MainApplication.class)
public class MainApplicationTests {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MainApplicationTests.class);
@Autowired
LogService1 logService1;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
log.info(logService1.getClass().getName());
logService1.method2();
}
}
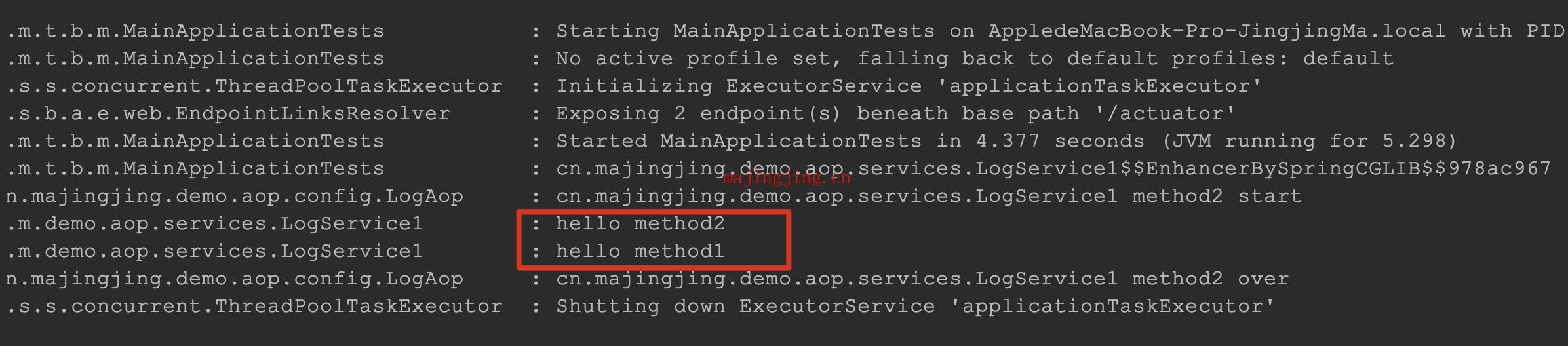
通过上面的日志, 我们可以看出, 方法内部的调用其实是没有被aop拦截到的. 这种场景 (时序图1)是我们的常规代码逻辑.看似加来aop的拦截,但就是不生效.
6 我们改造下程序
@Service
public class LogService2 {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogService2.class);
@LogToken
public void method1() {
log.info("hello method1");
}
@LogToken
public void method2() {
log.info("hello method2");
((LogService2) AopContext.currentProxy()).method1();
}
}
单元测试代码
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
log.info(logService1.getClass().getName());
logService1.method2();
log.info("---------");
log.info("---------");
log.info(logService2.getClass().getName());
logService2.method2();
}
再次运行,观察结果
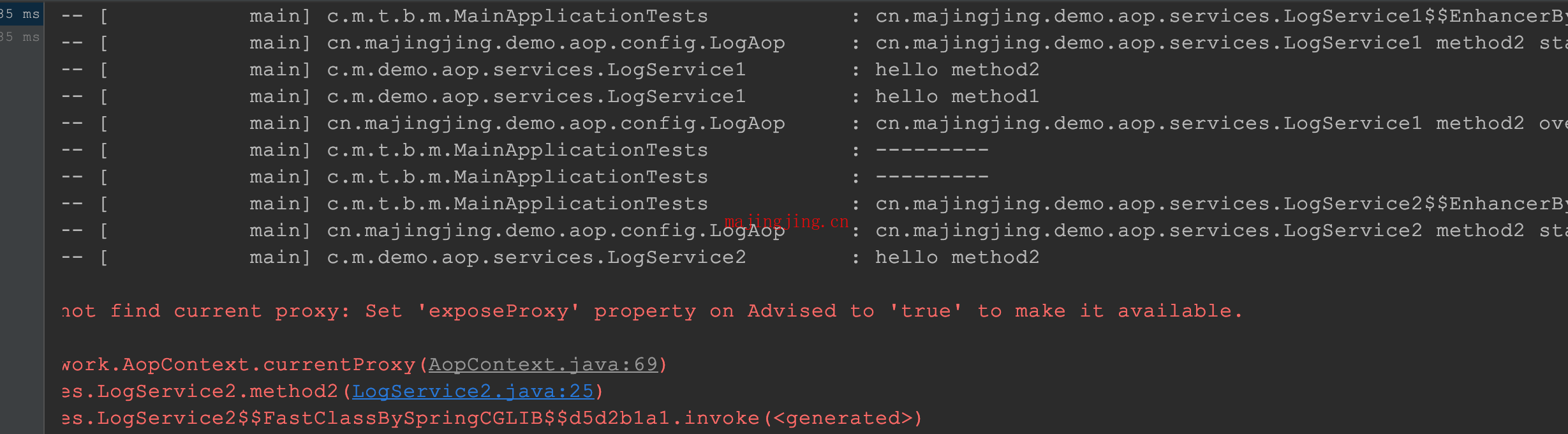 代码报错, 提示
代码报错, 提示 Set 'exposeProxy' property on Advised to 'true' to make it available. , 好的, 我们改下代码 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)
public class MainApplication {
...
}
再次运行,观察结果
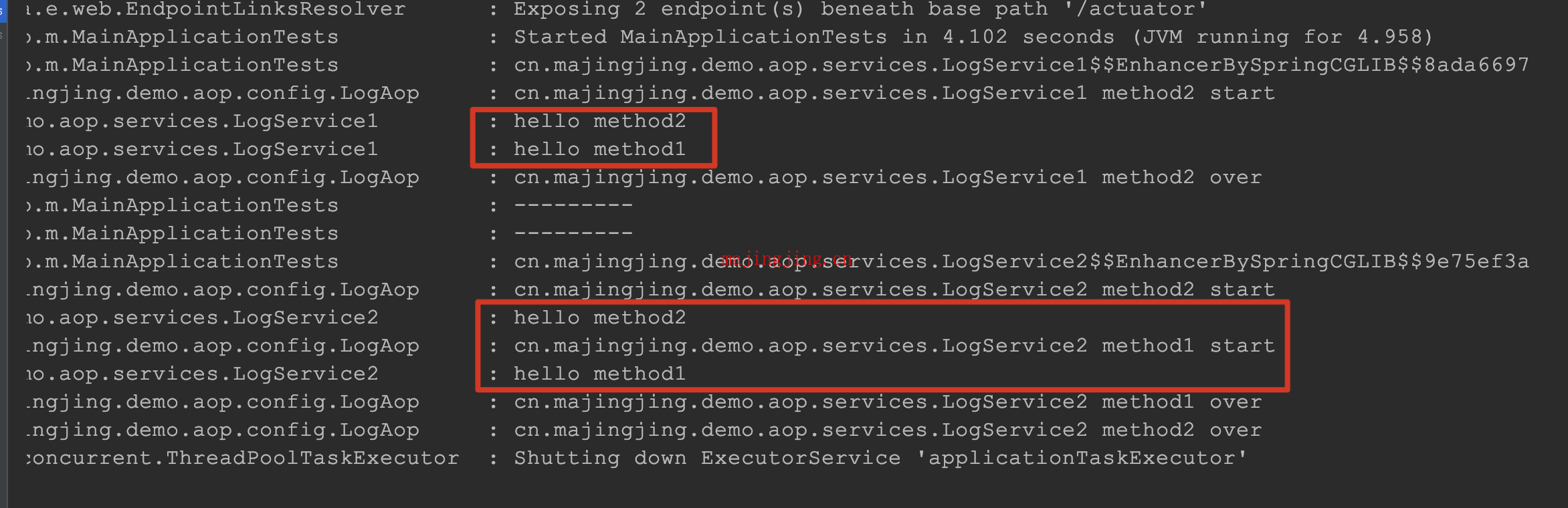 发现此时已经被拦截到了, 因为我们使用了代理对象
发现此时已经被拦截到了, 因为我们使用了代理对象((LogService2) AopContext.currentProxy())来调用method1(), 这次的代码流程如 (时序图2)
虽然这样是官方推荐的写法, 但是这样看上去不是很优雅的感觉. 让我们再看下如下代码.
7 再改下代码
@Service
public class LogService3 {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogService3.class);
@Autowired
LogService3 thisProxy;
@LogToken
public void method1() {
log.info("hello method1");
}
@LogToken
public void method2() {
log.info("hello method2");
thisProxy.method1();
}
}
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
log.info(logService1.getClass().getName());
logService1.method2();
log.info("---------");
log.info("---------");
log.info(logService2.getClass().getName());
logService2.method2();
log.info("---------");
log.info("---------");
log.info(logService3.getClass().getName());
logService3.method2();
}
再次运行,观察结果
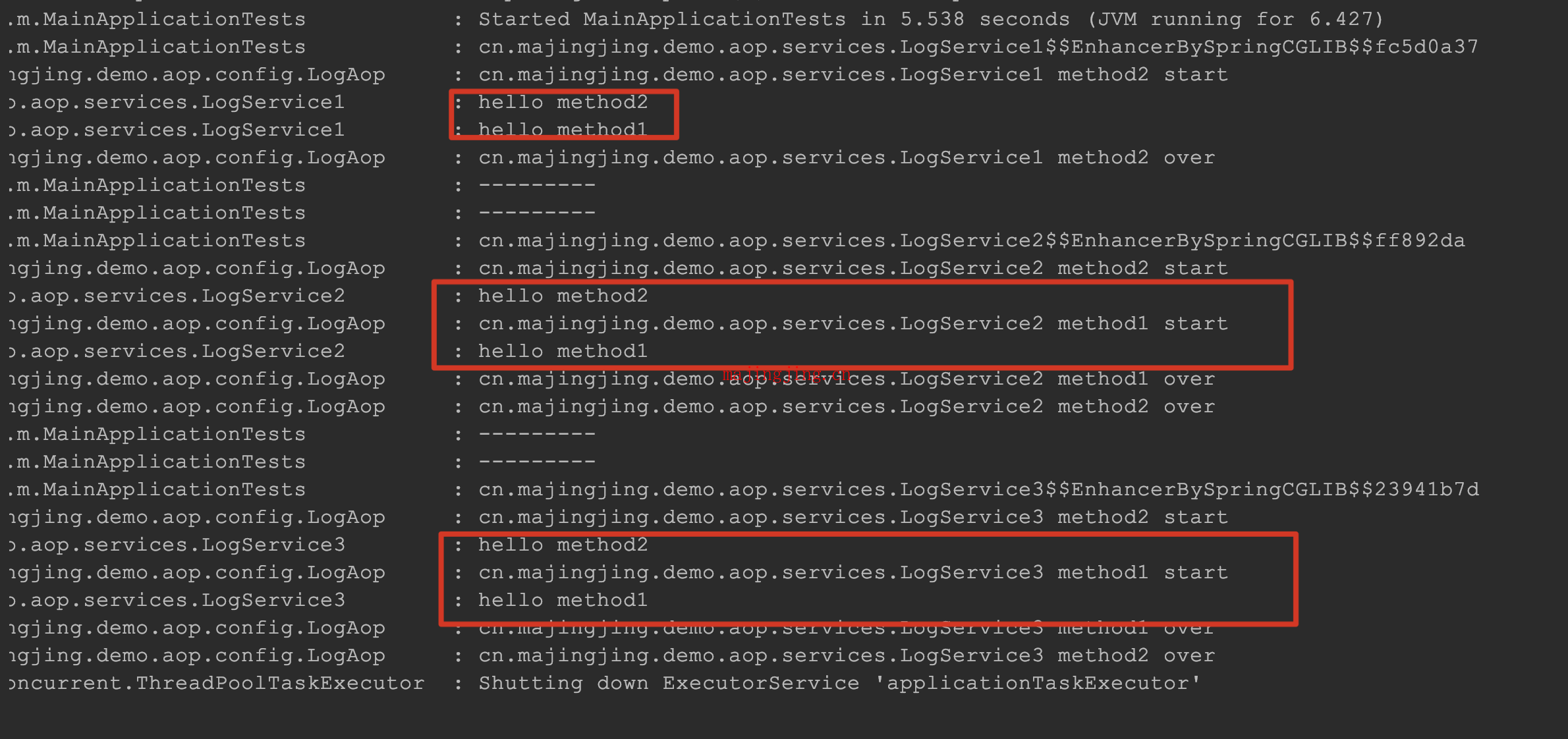 此时的
此时的LogService3也是可以被aop再次拦截到的. 因为我们将自己注入给了自己,此时的自己(@Autowired LogService3 thisProxy 这应该是sping3.x之后支持的自己注入给自己的特性)是被spring代理过的对象.
综上所描述的示例, 我们可以清晰的了解到方法内部到调用何时会被代理到,而何时又不会被代理到.
题外话:这里还是再讲下有些同学会问到的事务不生效的问题.
@Service
public class TransService {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TransService.class);
@LogToken
public void method1() {
log.info("hello method1");
}
@LogToken
public void method2() {
log.info("hello method2");
this.method1();
}
public void method3() {
log.info("hello method3");
this.method1();
}
}
@Test
public void transTest() {
transService.method2();
log.info("---------");
log.info("---------");
transService.method3();
}
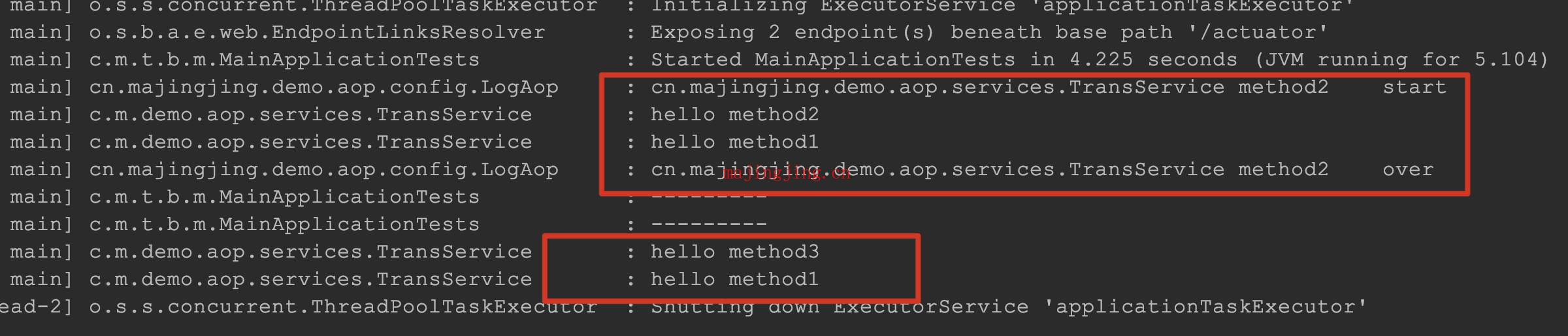
transService.method3();这样事务是不会生效的, 因为代理对象在这个方法上没有事务
示例代码: https://gitee.com/majj-demo/springboot-aop-demo
 打赏下吧
打赏下吧

